Company:
Midwest USA Utility
Machine Description:
Hydrogen-cooled Generator, 301.2MVA, 18kV, 2-pole,
End Winding Vibration Monitoring History And Failure Mechanism:
The utility had an outage in November of 2011 to perform maintenance on the 18 kV turbine generator which included reinforcement of the endwinding structure and the addition of Iris Power fiber optic endwinding vibrations ensors (EVAII sensors).
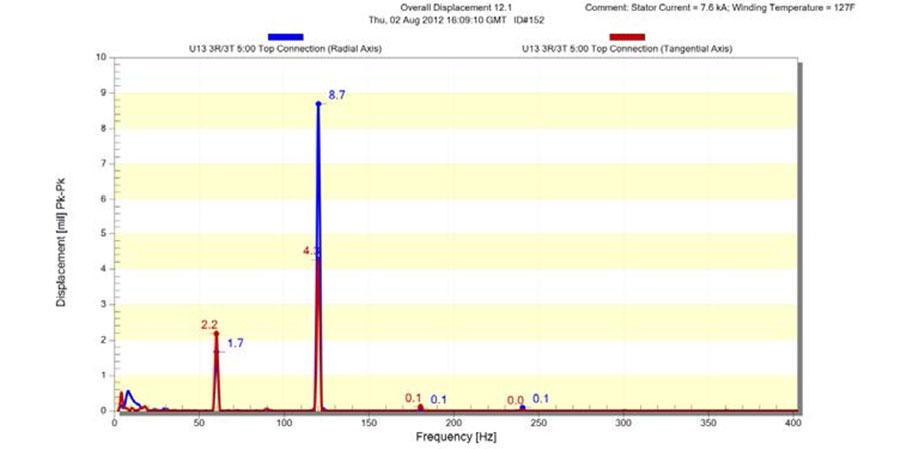
In August 2012, Ten months after the installation of the endwinding vibration monitoring sensors, there was data collected that showed 12.1mils (308μm) pk-pk overall displacement in the radial direction. While there is no formal standard identifying acceptable endwinding vibration levels, Iris Power indicated but displacement higher than 10mils (250μm) pk-pk overall is concerning.
Overall Displacement Spectra
Visual inspection of the windings in showed dusting near one of the phase connections being monitored in the 5:00 position.
Dusting Between Felt Block and Stator End Cap

The dusting is an indication of the stator bars relative motion at their supports and insulation abrasion. Further, copper can eventually fatigue and fail from small stress amplitudes due to high cycle fatigue. The generator could then failure as a result of phase to phase faults or broken conductors. The vibration signature indicated the onset of excessive movement and was confirmed visually. The excessive movement should be limited to prevent failure and the vibration should be monitored continuously to indicate any change to the endwinding support system.

